Start¶
See also
- Official ReactiveX documentation: Start
-
classmethod
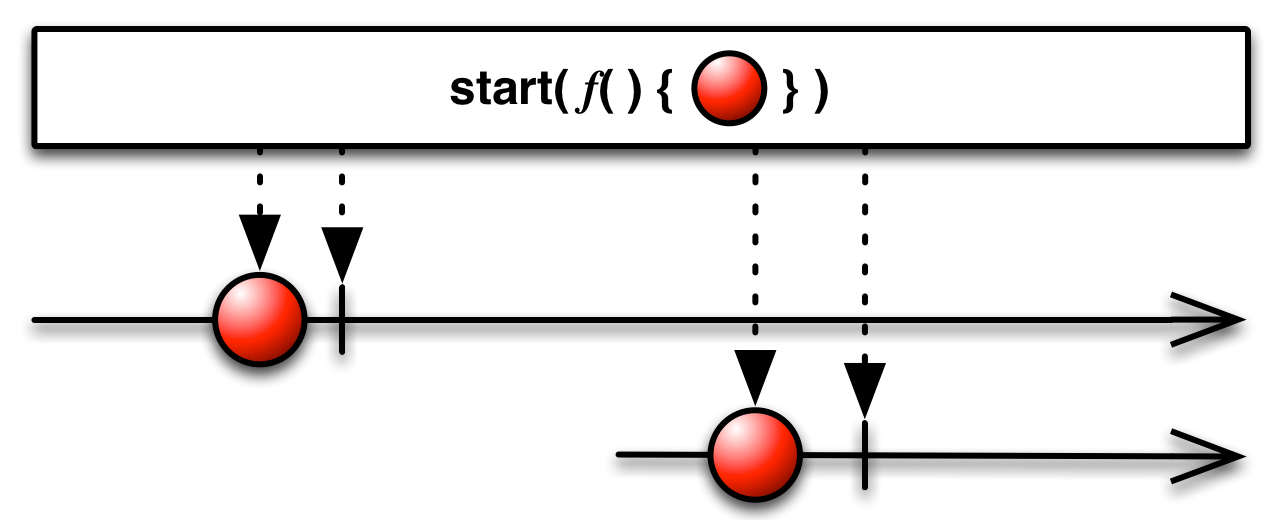
Observable.start(func, scheduler=None)¶ Invokes the specified function asynchronously on the specified scheduler, surfacing the result through an observable sequence.
Example: res = rx.Observable.start(lambda: pprint(‘hello’)) res = rx.Observable.start(lambda: pprint(‘hello’), rx.Scheduler.timeout)
Keyword arguments: func – {Function} Function to run asynchronously. scheduler – {Scheduler} [Optional] Scheduler to run the function on. If
not specified, defaults to Scheduler.timeout.Returns {Observable} An observable sequence exposing the function’s result value, or an exception.
Remarks: The function is called immediately, not during the subscription of the resulting sequence. Multiple subscriptions to the resulting sequence can observe the function’s result.
-
classmethod
Observable.start_async(function_async)¶ Invokes the asynchronous function, surfacing the result through an observable sequence.
Keyword arguments: :param types.FunctionType function_async: Asynchronous function which
returns a Future to run.Returns: An observable sequence exposing the function’s result value, or an exception. Return type: Observable 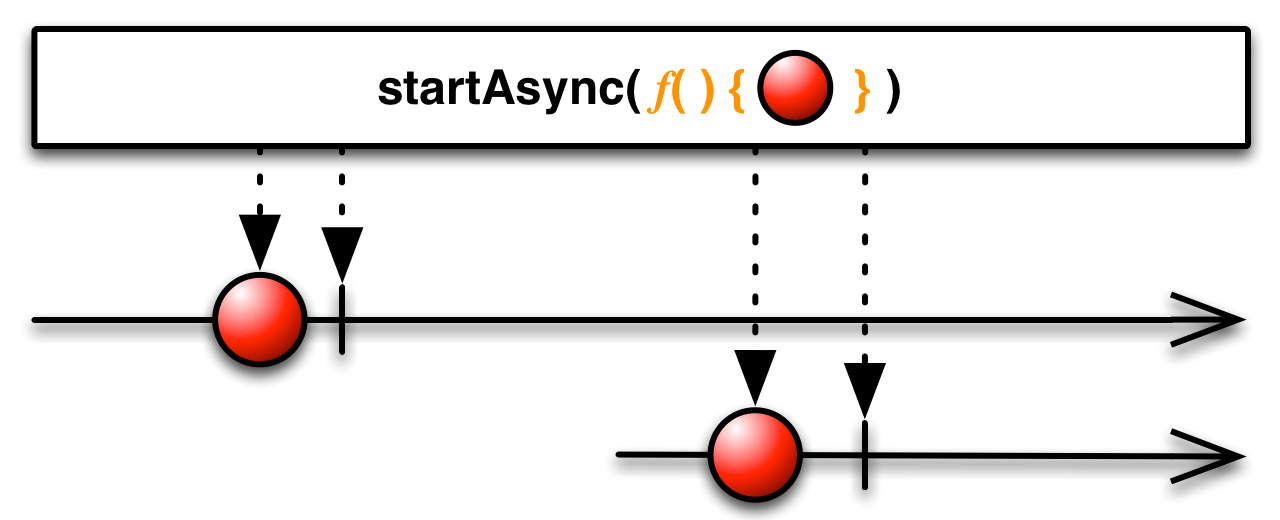
-
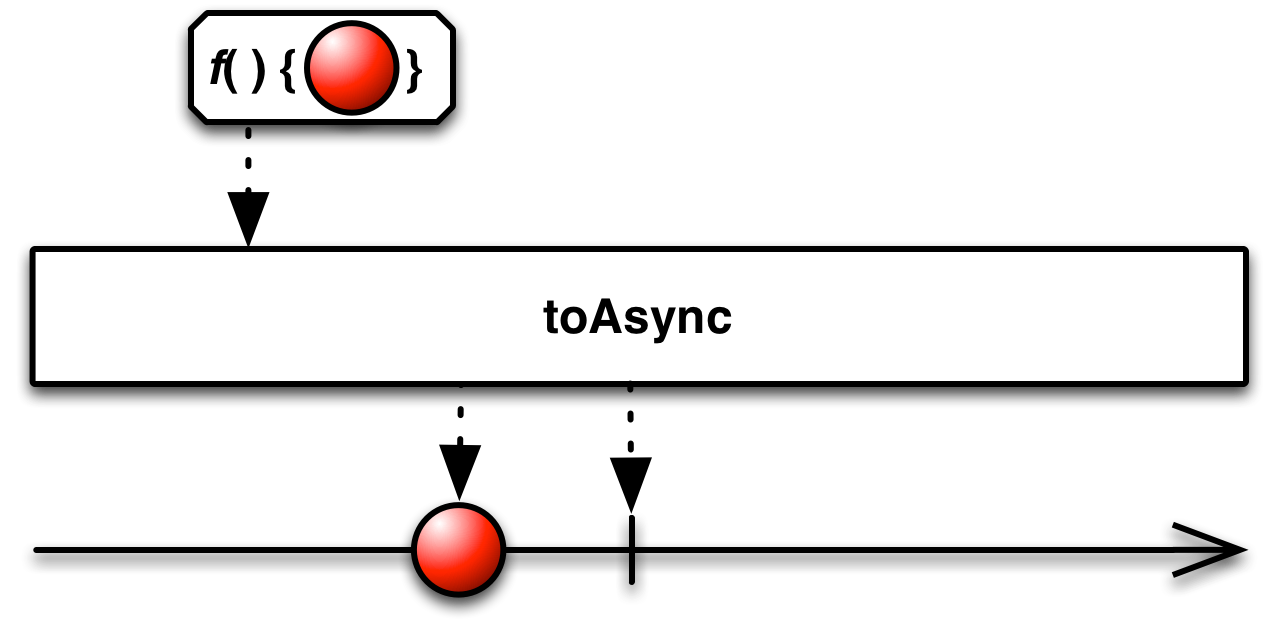
classmethod
Observable.to_async(func, scheduler=None)¶ Converts the function into an asynchronous function. Each invocation of the resulting asynchronous function causes an invocation of the original synchronous function on the specified scheduler.
Example:
res = Observable.to_async(lambda x, y: x + y)(4, 3) res = Observable.to_async(lambda x, y: x + y, Scheduler.timeout)(4, 3) res = Observable.to_async(lambda x: log.debug(x), Scheduler.timeout)('hello')
Parameters: func (types.FunctionType) – Function to convert to an asynchronous function. Keyword Arguments: scheduler (Scheduler) – Scheduler to run the function on. If not specified, defaults to rx.Scheduler.timeout().Returns: Asynchronous function. Return type: (types.FunctionType)